Welcome
Why nlmixr?
The goal of nlmixr, or more accurately nlmixr2, is to support easy and robust nonlinear mixed effects models (NLMEMs) in R.
NLMEMs are used to help identify and explain the relationships between drug exposure, safety, and efficacy and the differences among population subgroups. Most often, they are built using longitudinal PK and pharmacodynamic (PD) data collected during clinical studies. These models characterize the relationships between dose, exposure and biomarker and/or clinical endpoint response over time, variability between individuals and groups, residual variability, and uncertainty.
NLMEM development in the pharmaceutical space is dominated by a small number of proprietary, commercial software tools. Although this kind of approach to software has some advantages, adopting an open-source, open-science paradigm also has benefits - third-party auditing or adjustments are possible, and the precise model-fitting methodology employed can be determined by anyone with the time and energy to review the source code. We see nlmixr2 being especially useful in being able to integrate into the rich R ecosystem, and it is well suited for use in scripted, literate-programming workflows of the kind flourishing in the R ecosystem by means of packages such as knitr and rmarkdown.
The nlmixr2 blog
laplace and agq estimation methods
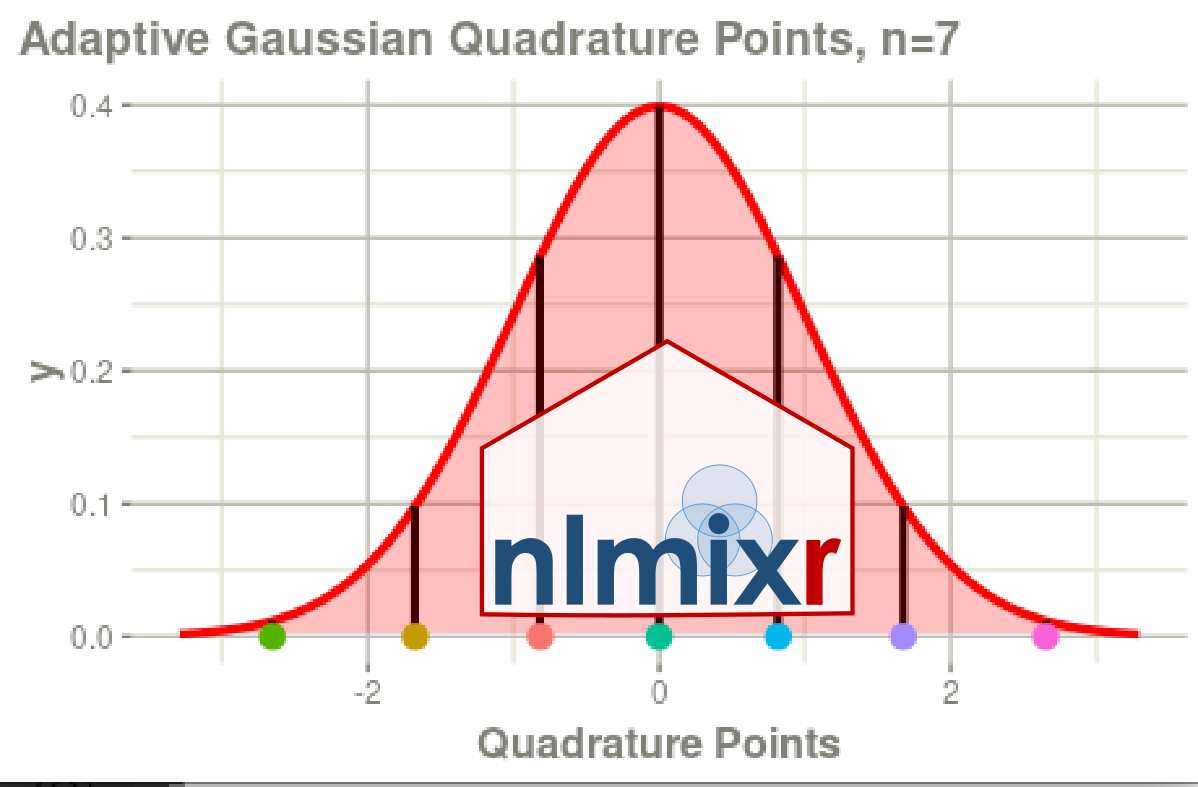
nlmixr2 log-likelihood In 2022 we announced the focei log-likelihood. However, in our last advisory committee meeting Mats Karlsson pointed out that focei log-likelihood may not be the best approach. He believed that Stuart L. Beal and Lewis B. Sheiner did not include this method since they may have been trying to protect users from methods that may not make sense (for example, maybe focei log-likelihood is not an accurately enough approximation of the likelihood).
Read more